Complete STI/STD Test
Complete STI/STD Test
Unable to load pickup availability
This test kit allows:
This test kit allows:
🟡 Collection of the first morning urine
🏠 Easy and quick blood collection at home
🧪 Reliable Laboratory Results
🕐 Results by email within 5 business days of receiving your sample
Tested parameters
Tested parameters
Blood Collection: Hepatitis B Virus (HBV); Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Urine Collection : Chlamydia; Trichomoniasis; Gonorrhea; Syphilis; Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1); Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma hominis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Ureaplasma parvum, Haemophilus ducreyi
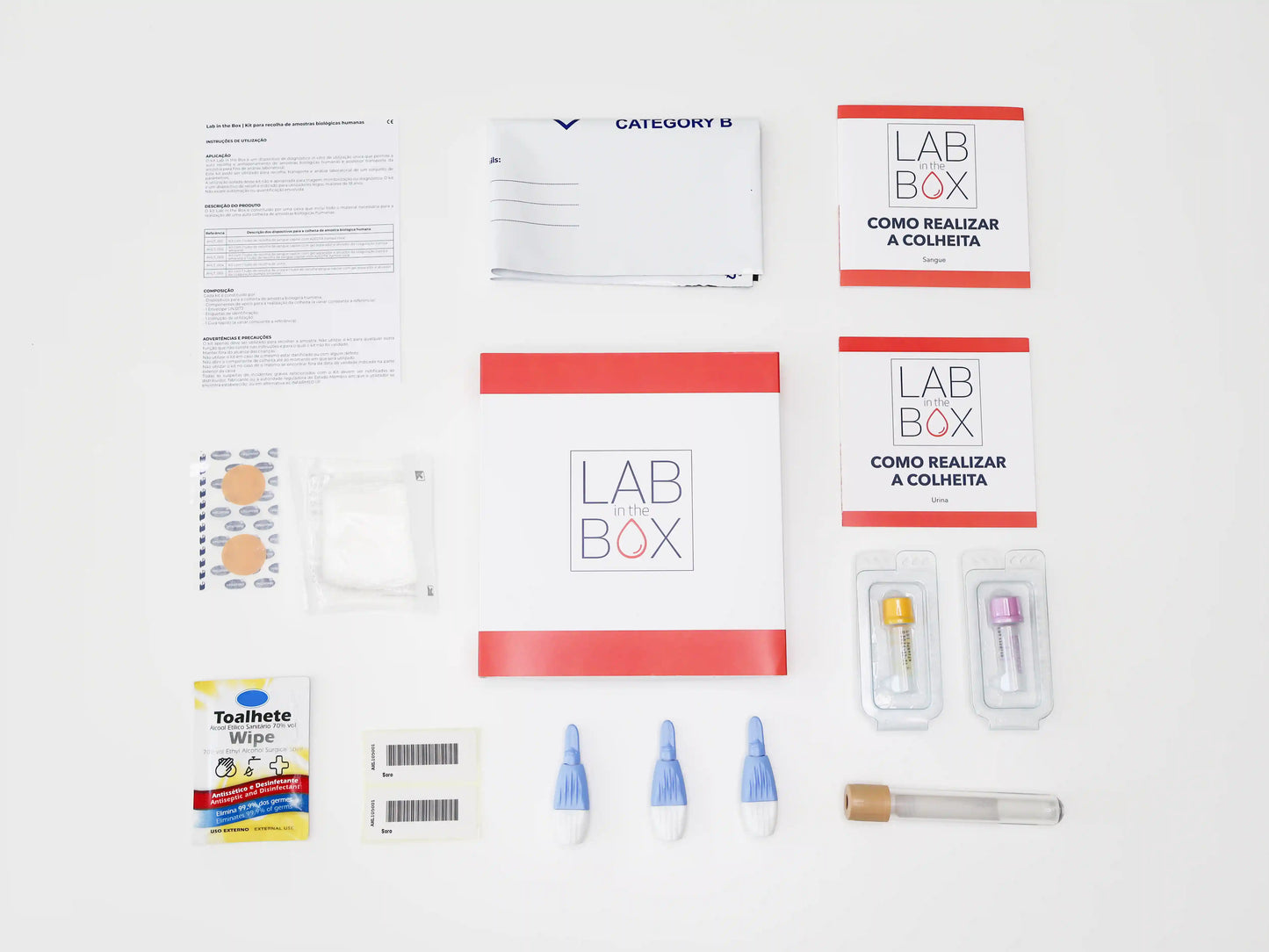
What is included in the test:
What is included in the test:
☑️ The kit includes all the necessary material for sample collection and shipping;
☑️ Cost of sending the kit back to the laboratory;
☑️ Detailed instructions and training videos;
☑️ Digital results;
☑️ Specialized support if necessary.
When to test
When to test
The collection must be carried out before 11:30 am on a Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday and returned on the same day by post at a delivery point or by scheduling a collection by 12 pm.
Amount of blood to be collected:
Amount of blood to be collected:
You must use the yellow-tapped collection tube and collect a minimum amount of blood of 600 μL.
Fast:
Fast:
Fasting is not necessary to perform this test.



Who should get an STI/STD test?
- People with associated symptoms: itching, pain during sexual intercourse, warts or rashes in the genital and anal region, abnormal discharge, bleeding outside the menstrual period, testicular inflammation;
- People without symptoms, but who have engaged in risky sexual behavior.
When should we take our STI/STD test?
Taking care of your health is an act of self-love and
responsibility. There are many reasons why you should consider doing this. Let's explore some:
- New Relationship: Before starting a new phase with someone special, it is important to ensure the health of both of you.
- Healthy Pregnancy: If you are planning a pregnancy or are already pregnant, knowing your status can ensure a healthy future for you and your baby.
- Concern for Well-Being: Staying informed about your health brings peace of mind, regardless of the outcome.
- Risky Sexual Contact: If you have had any risky sexual contact, whether vaginal, anal or oral, it is essential to know your status.
- Preventing Contagion: Protecting your health and that of others is essential. By knowing your status, you can make informed decisions to prevent transmission of the virus.
Sexually Transmitted Infections Tested
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus that attacks the liver and can cause acute or chronic disease. Most of the time, hepatitis B is acute and does not require any specific treatment, and the virus is eventually eliminated by the immune system. However, in some cases, hepatitis B becomes chronic.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
HIV is the human immunodeficiency virus that causes AIDS. The virus attacks and destroys our body's immune system, that is, it destroys the defense mechanisms that protect us from diseases.
Chlamydia
Infection that can affect various areas of the body and is usually located in the mouth, penis, vagina or anus. If left untreated, it can lead to ectopic pregnancies, infertility and chronic pelvic or abdominal pain.
Trichomoniasis
Parasitic infection that causes pain, itching and increased discharge in the urogenital region. It can lead to the development of urethritis, vaginitis or, occasionally, cystitis, epididymitis or prostatitis.
Gonorrhea
Infection of epithelial cells mainly of the urethra, cervix, anus and oropharynx. It is one of the main causes of urethritis.
Syphilis
Infection characterized by 3 sequential, symptomatic phases separated by periods of asymptomatic latent infection. Common symptoms include genital ulcers, skin lesions, meningitis, aortic disease, and neurological syndromes.
Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
Recurrent infection affecting the skin, oral cavity, lips, eyes, and genitals. HSV-1 causes gingivostomatitis, cold sores, and herpes keratitis. HSV-2 usually causes genital lesions.
Genital Mycoplasmosis
Infection of the urogenital system, which causes pain, itching and difficulty urinating.
Mycoplasma hominis
Infection of the lower genital tract that can cause a variety of infections such as vaginosis, cervicitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease. It is also associated with infertility and pregnancy complications.
Ureaplasma urealyticum
Infection of the urogenital tract, which causes pain, itching and increased discharge.
Ureaplasma parvum
Infection of the urogenital tract, which causes pain, itching and increased discharge.
Haemophilus ducreyi
Bacteria that causes infection of the genital mucosa, characterized by papules, painful ulcers and enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes.


